Distance measurement and object detection play an important role in many fields, including factory automation, robotics applications, and logistics. Especially in the field of security applications, there is a need to detect and respond to objects or people at specific distances. For example, a robotic arm may need to stop operating as soon as a worker enters a hazardous area.
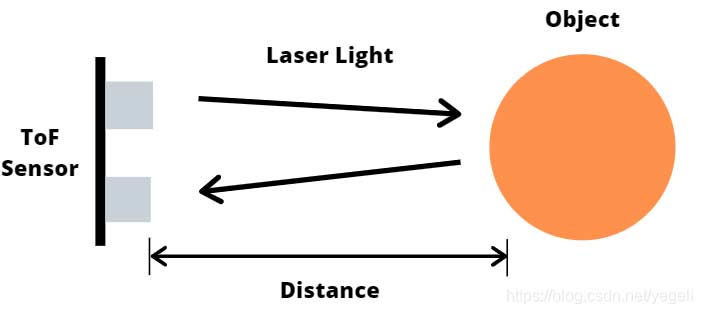
Therefore, ToF sensors are becoming more and more important. With ToF technology, light is emitted from a modulated light source, such as a laser, and the beam is reflected by one or more objects and captured by a sensor or camera. ToF sensor can determine the distance by the time delay between the emitted light and the received emitted light. The time delay is proportional to twice the distance (round trip) between the camera and the object. So, the distance can be estimated as depth d = (c × Δt)/2, where c is the speed of light. ToF cameras output 2D data along with the required depth information.
ToF sensor allows recording the entire image at once. No progressive scanning is required, nor is there any relative motion between the sensor and the object being observed. ToF sneosr is usually classified as LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), but it is actually a method based on flash LIDAR, not scan LIDAR. There are basically two different methods of measuring the time-of-flight of optical pulses using ToF: a pulsed mode of operation based on charge-coupled device (CCD) technology and a continuous wave (CW) mode of operation.